Rules¶
These settings simplify the configuration work required for
each analysis by establishing how to interpret raw data
entered during new analyses.
By implementing specific rules for sample names, sample IDs,
or file names,
you can automatically exclude unnecessary samples like washes,
determine sample types (Standard/QC/Unknown),
specify reference samples, and input concentrations.
Furthermore, by registering internal standard (ISTD) information,
ISTDs can be automatically identified according to these rules.
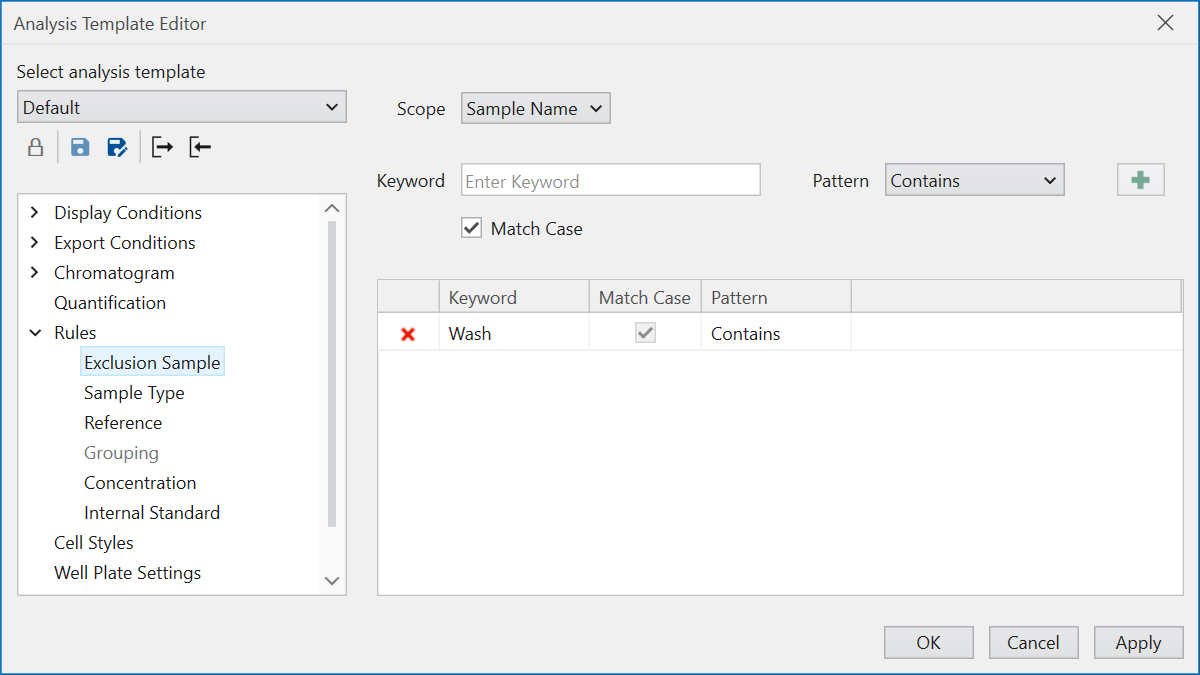
Exclusion Sample allows you to remove samples
you do not wish to analyze from the loaded raw data.
For instance, to exclude samples with “Wash” in their name,
select “Sample Name” under Scope in the UI,
and enter “Wash” as the Keyword.
By choosing “Contains” from Pattern and pressing the “+” button,
you add a condition to exclude samples containing the phrase “Wash”.
The “Match Case” option enables case-sensitive comparisons
between the names given by Keyword and Scope.
Patterns available for selection include “Contains”
(where the keyword is included), “Starts with”, “Ends with”,
and “Complete Match”.
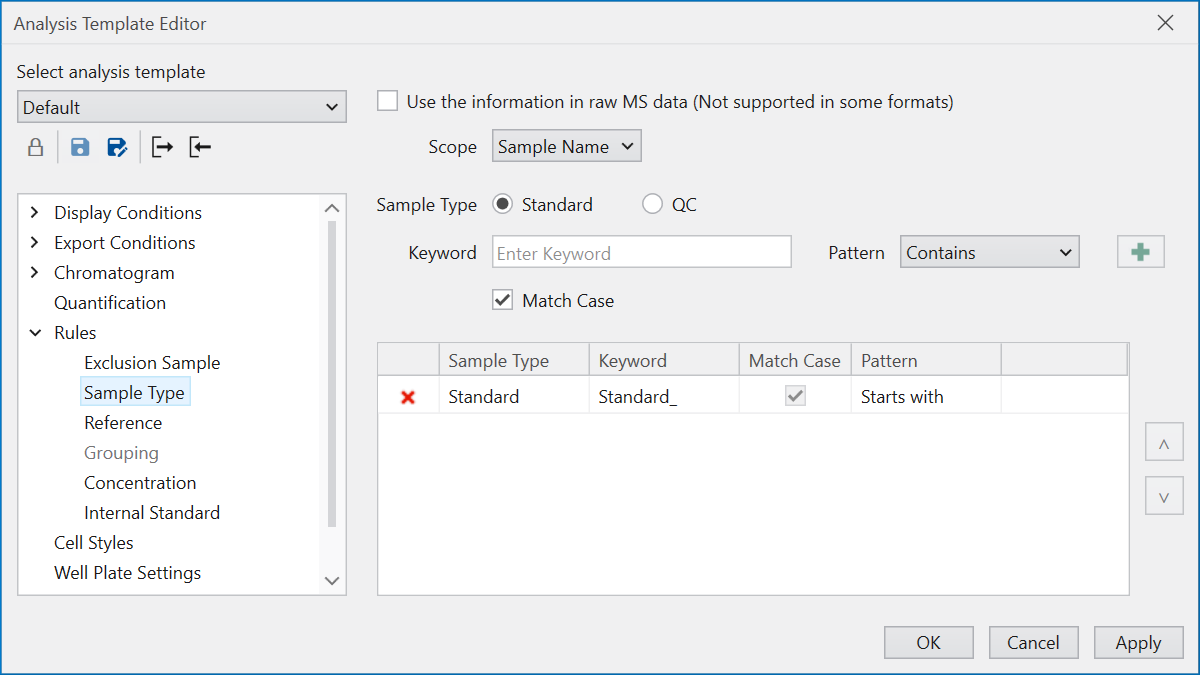
Sample Type automates the determination of
the necessary sample type for calibration curve creation
by defining rules to identify whether an analyzed sample is
Standard, QC, or Unknown.
“Use the information in raw MS data” attempts to recognize
the sample type noted within the raw data,
although it’s impotant to note that not all raw data formats
are supported.
This rule configuration is similar to Exclusion Sample,
but additional settings must be applied
to determine whether the sample type is Standard or QC
based on the specified conditions.
Samples not fitting into Standard or QC categories are
recognized as Unknown samples.
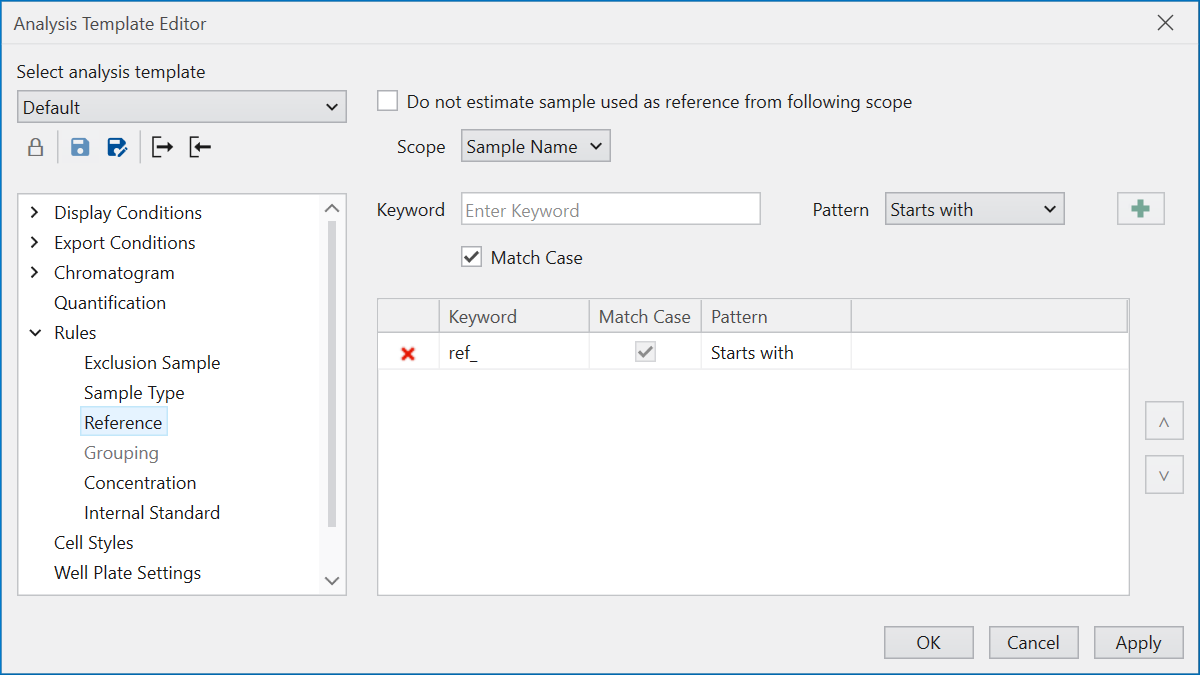
Reference standardizes the criteria for selecting reference samples.
Reference samples are used to compare the retention time (RT)
and peak shape against those detected in other samples,
facilitating the assessment of peak detection accuracy.
Additionally, reference samples can serve as supervisors
when performing
Supervised Detection
in new analyses or
reanalyses.
If you do not wish to use the predetermined conditions, tick
“Do not estimate sample used as reference from following scope”.
This option is designed for termporarily bypassing
reference judgement during activities such as
Reanalysis while retaining the rule settings.
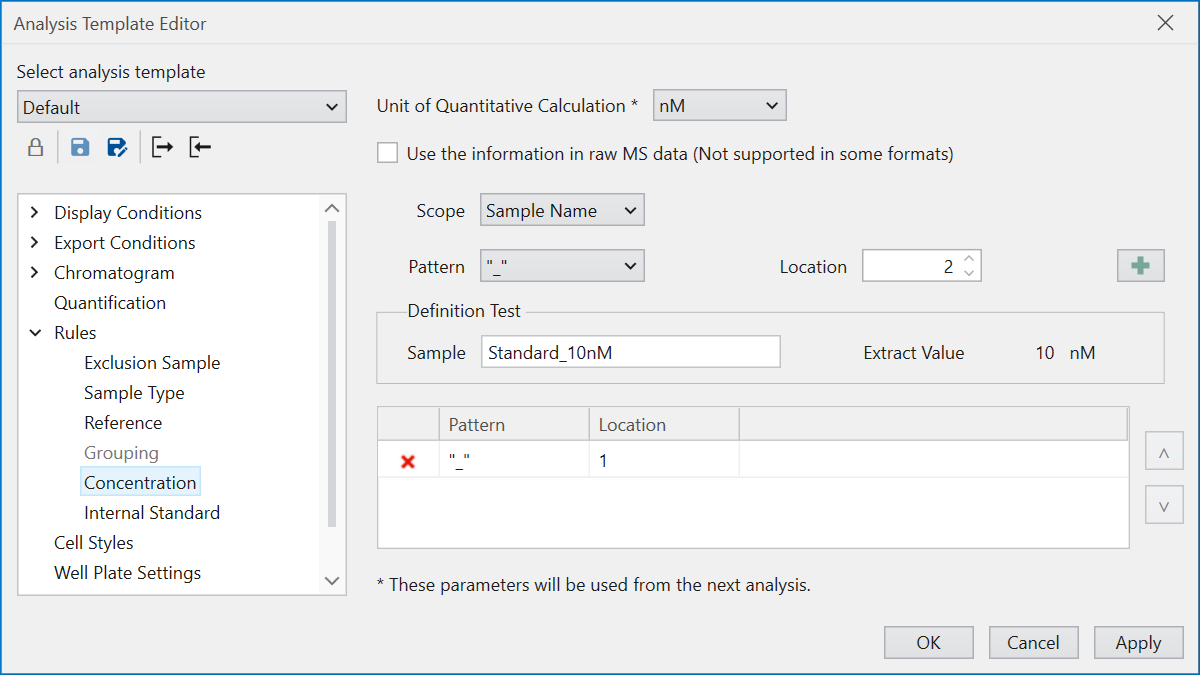
Concentration defines rules for extracting concentration values
from information within the raw data.
“Unit of Quantitative Calculation” allows for specification
of concentration unit.
Should the desired concentration unit not be listed,
it can be added through
Preference.
To determine the concentration value,
divide the string corresponding to the specified Scope
by the selected Pattern, and designate which part of
the divided string should be treated as the concentration value.
For example, if “Sample Name” is the Scope and
the name is “Standard_10nM”,
selecting “_” as the Pattern divides the name into
“Standard” and “10nM”.
By setting “Location” to 2 and pressing the “+” button,
you can register the condition, indicating that
“10nM” is the concentration value.
“Definition Test” is provided to ensure correct condition setting.
Inputting a string that matches the Scope into the Sample field
allows for the simulation of the concentration value extraction
based on the condition,
making it advisable to verify before registering the conditions.
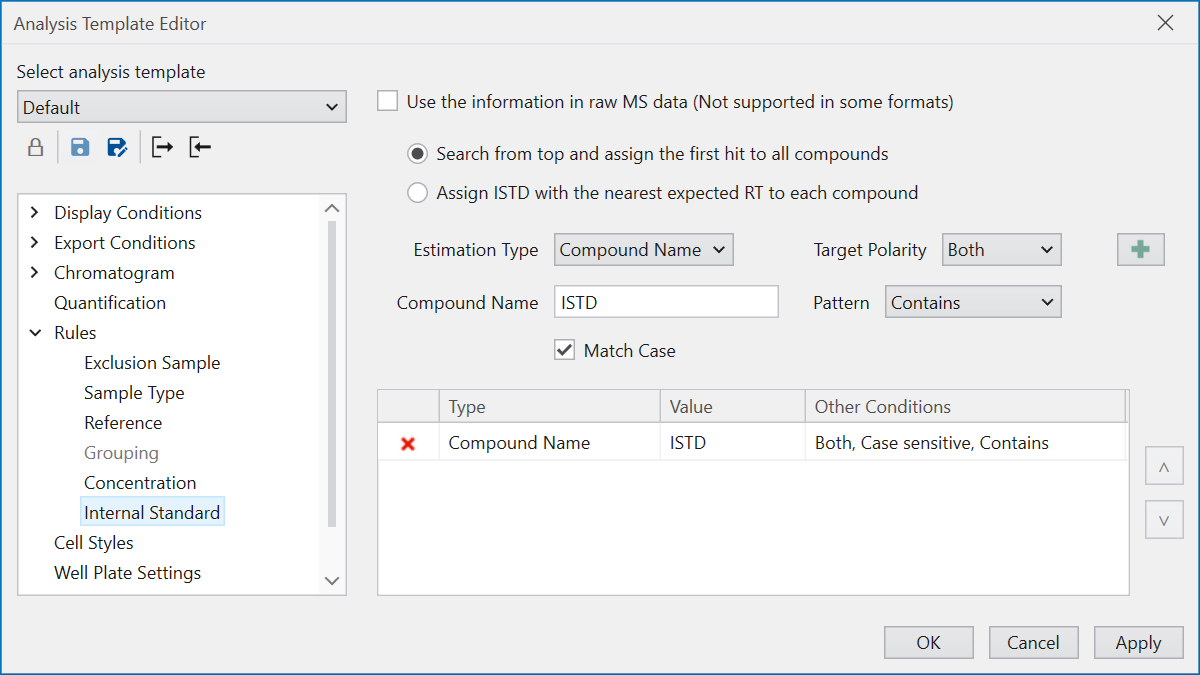
Internal Standard pre-registers compounds as
internal standards (ISTDs),
setting rules to identify during analysis whether
a compound is an ISTD or a target for quantification.
“Use the information in raw MS data” attempts to recognize
whether a compound is an ISTD based on written information,
but as it does not support all raw data formats,
caution is advised.
To decide if a compound is an ISTD,
choose the rule type under “Estimation Type”:
Compound Name, MRM/SRM/PRM, SIM/Scan,
and select the applicable Polarity.
For Compound Name, input the judgement condition
based on string information as with other rule settings.
For other types, input values relevant to the analysis conditions,
like Q1 and Q3 values.
Select the method for assigning determined ISTDs
to target compounds using the ratio button.
Choosing “Search from top and assign the first hit to all compounds”
evaluates ISTD determination conditions from the top,
assigning the first matching compound as the ISTD.
This process is conducted for each polarity,
with each polarity’s ISTD serving all compounds of that polarity.
Selecting “Assign ISTD with the nearest expected RT
to each compound” considers all compounds meeting
the ISTD criteria as ISTDs.
For each polarity, it matches target compounds and ISTDs
based on closely related Expected RT values,
assigning the appropriate ISTD to each target compound.